Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ieda, Junichi; Yamane, Yuta*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 symmetry in a tetragonal phase of BaCo
symmetry in a tetragonal phase of BaCo Ni
Ni S
S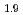
Shamoto, Shinichi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ieda, Junichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Kei; Yu, W.*; Xu, M.*; Puebla, J.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Bauer, G.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Substitutions of In sites by Zn atoms in heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn is reported to induce an antiferromagnetic order by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki University. Near the critical region, non-Fermi-liquid behavior has been observed in magnetization and specific heat. We have performed NMR measurements to reveal the spin fluctuations near the critical region.
is reported to induce an antiferromagnetic order by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki University. Near the critical region, non-Fermi-liquid behavior has been observed in magnetization and specific heat. We have performed NMR measurements to reveal the spin fluctuations near the critical region.
Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Garst, M.*; Gegenwart, P.*; Bud'ko, S. L.*; Canfield, P. C.*
no journal, ,
Bicritical points, at which two distinct symmetry-broken phases become simultaneously unstable, are typical for spin-flop metamagnetism. Interestingly, the heavy-fermion compound YbAgGe also possesses such a bicritical point (BCP) with a low temperature 0.3K at a magnetic field of 4.5T. In its vicinity, YbAgGe exhibits anomalous behavior that we attribute to the influence of a quantum bicritical point that is close in parameter space yet can be reached by tuning 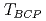 further to zero. Using high-resolution measurements of the magnetocaloric effect, we demonstrate that the magnetic Gruneisen parameter
further to zero. Using high-resolution measurements of the magnetocaloric effect, we demonstrate that the magnetic Gruneisen parameter  indeed both changes sign and diverges as required for quantum criticality. Moreover,
indeed both changes sign and diverges as required for quantum criticality. Moreover,  displays a characteristic scaling behavior but only on the low-field side
displays a characteristic scaling behavior but only on the low-field side 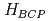 , indicating a pronounced asymmetry with respect to the critical field. We speculate that the small value of
, indicating a pronounced asymmetry with respect to the critical field. We speculate that the small value of 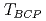 is related to the geometric frustration of the Kondo lattice of YbAgGe.
is related to the geometric frustration of the Kondo lattice of YbAgGe.

Tokunaga, Yo
no journal, ,
NMR studies have been performed on a newly discovered heavy fermion superconductor UTe . Using a single crystal, we have successfully measured the NMR Knight shift and spin-lattice relaxation rate for fields along the three orthorhombic crystal axes. The data confirm a moderate Ising anisotropy for both the static and dynamical susceptibilities in the paramagnetic state above about 20 K. However, a divergence of the spin-spin relaxation rate observed below 20 K for H//a demonstrates the development of strong longitudinal magnetic fluctuations along the a-axis at very low frequency.
. Using a single crystal, we have successfully measured the NMR Knight shift and spin-lattice relaxation rate for fields along the three orthorhombic crystal axes. The data confirm a moderate Ising anisotropy for both the static and dynamical susceptibilities in the paramagnetic state above about 20 K. However, a divergence of the spin-spin relaxation rate observed below 20 K for H//a demonstrates the development of strong longitudinal magnetic fluctuations along the a-axis at very low frequency.
 on Pd(210)
on Pd(210)Ueta, Hirokazu; Sasakawa, Yuya*; Ivanov, D.*; Ono, Satoshi*; Ogura, Shohei*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kubota, Masato; Kato, Seiichi*; Nigo, Seisuke*; Amemiya, Kenta*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Takuma*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
A muon ( ) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion (
) having 207 times larger mass of electron and the same charge as the electron has been known to catalyze a nuclear fusion ( CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed
CF) between deuteron (d) and triton (t). In this work, we have solved simultaneous reaction rate equations by the 4th-order Runge-Kutta method for the jointed  CF cycles in the two layers (H
CF cycles in the two layers (H /D
/D and D
and D /T
/T ). The T
). The T concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
concentration to maximize the intensities of fusion neutrons and muons emitted to the vacuum will be discussed.
 CF experiment at J-PARC MLF
CF experiment at J-PARC MLFNatori, Hiroaki*; Doiuchi, Shogo*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Miyashita, Konan*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Nagatani, Yukinori*; Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Oka, Toshitaka; et al.
no journal, ,
A muonic molecule which consists of muon and two hydrogen isotope nuclei (deuteron (d) or tritium (t)) decays immediately via nuclear fusion (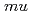 CF) and the muon will be released as a recycling muon. We attempted to use these muons to develop the scanning muon microscope. In this work, we will report the detection of neutron which emits during the
CF) and the muon will be released as a recycling muon. We attempted to use these muons to develop the scanning muon microscope. In this work, we will report the detection of neutron which emits during the  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Nagai, Yuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalized fusion ( CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we attemped to observe a released muon after intermolecular nuclear reaction using muonic X-ray.
CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we attemped to observe a released muon after intermolecular nuclear reaction using muonic X-ray.
 CF experiment at J-PARC MLF
CF experiment at J-PARC MLFOkutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Muon catalized fusion ( CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we discussed how to observe a kinetic energy distribution of a recycling muon emitted after
CF) is expected to be a high-quality muon beam source for undestructive measurement and a monoenergetic neutron source. In this work, we discussed how to observe a kinetic energy distribution of a recycling muon emitted after  CF reaction.
CF reaction.
Miyashita, Konan*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Nakashima, Ryota*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
To observe a kinetic energy distribution of a recycling muon emitted after  CF reaction, it is necessary to guide the recycling muons to a detector. In this work, we simulated the muon transportation using PHITS code and designed an experimental system.
CF reaction, it is necessary to guide the recycling muons to a detector. In this work, we simulated the muon transportation using PHITS code and designed an experimental system.
Nakashima, Ryota*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Miyashita, Konan*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Okada, Shinji*; Sato, Motoyasu*; Oka, Toshitaka; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
The recycling muon emitted after the muon catalized fusion ( CF) has a kinetic energy between a few keV to 10 keV. To observed the kinetic energy distribution of the recycling muon, we have to guide and inject muons to Ti foil, and measure the muonic X-ray. In this work, we utilized SIMION code to calculate the electric field and the trajectory of muons from deuteron target to Ti foil.
CF) has a kinetic energy between a few keV to 10 keV. To observed the kinetic energy distribution of the recycling muon, we have to guide and inject muons to Ti foil, and measure the muonic X-ray. In this work, we utilized SIMION code to calculate the electric field and the trajectory of muons from deuteron target to Ti foil.
Kajimoto, Ryoichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Al
Al , 3
, 3Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Masuda, Hayato*; Higashinaka, Ryuji*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*
no journal, ,
SmAu Al
Al exhibits antiferromagnetic order near 2.8 K at atmospheric pressure. The specific heat C/T is a heavy electron system with a low temperature of 2J/molK
exhibits antiferromagnetic order near 2.8 K at atmospheric pressure. The specific heat C/T is a heavy electron system with a low temperature of 2J/molK or more. This heavy electronic state is insensitive to magnetic field. In particular, this compound is characterized in that the heavy electronic state depends on the magnetic field direction. However, it is also interesting that the valence of Sm does not seem to be mixed valance state only in 3+ state according to XAS. Therefore, in this study, we attempted to estimate the temperature and magnetic field direction dependence of magnetic fluctuations using Al-NMR. This time, we discuss spin lattice relaxation time.
or more. This heavy electronic state is insensitive to magnetic field. In particular, this compound is characterized in that the heavy electronic state depends on the magnetic field direction. However, it is also interesting that the valence of Sm does not seem to be mixed valance state only in 3+ state according to XAS. Therefore, in this study, we attempted to estimate the temperature and magnetic field direction dependence of magnetic fluctuations using Al-NMR. This time, we discuss spin lattice relaxation time.
 with noncentrosymmetric crystal structure probed by
with noncentrosymmetric crystal structure probed by  SR
SRMiyazaki, Itsuki; Higemoto, Wataru; Ito, Takashi; Isobe, Masaaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Araki, Yasufumi; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei; Yasui, Shigehiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kaneko, Koji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Ba
Ba Nb
Nb O
O in high-temperature phase
in high-temperature phaseYoneda, Yasuhiro; Fu, D.*
no journal, ,
Ca Ba
Ba Nb
Nb O
O (CBN) in which Ba of BaNb
(CBN) in which Ba of BaNb O
O is replaced with Ca, which is a ferroelectric substance having a tungsten bronze structure, A single-phase tetragonal phase appears in the composition range where the amount of Ca substitution is 0.19
is replaced with Ca, which is a ferroelectric substance having a tungsten bronze structure, A single-phase tetragonal phase appears in the composition range where the amount of Ca substitution is 0.19 
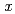
 0.32. For CBN, superlattice reflection appears in the powder X-ray diffraction pattern even in ceramic samples. There is a long-period structure that is deviated from the average structure. Since superlattice reflection is still observed in the high-temperature phase, structural analysis was performed in the high-temperature phase. It was found that the average structure of the high-temperature phase well reflected the local structure of the room temperature phase. It is considered to be a phenomenon that reflects the reentrant phase transition peculiar to tungsten bronze.
0.32. For CBN, superlattice reflection appears in the powder X-ray diffraction pattern even in ceramic samples. There is a long-period structure that is deviated from the average structure. Since superlattice reflection is still observed in the high-temperature phase, structural analysis was performed in the high-temperature phase. It was found that the average structure of the high-temperature phase well reflected the local structure of the room temperature phase. It is considered to be a phenomenon that reflects the reentrant phase transition peculiar to tungsten bronze.